Automate GitHub Backups
Why automation beats cron
Shell scripts and git clone --mirror jobs work until they don’t—usually when GitHub rotates tokens, repositories rename, or metadata gets missed. Gitea Mirror bundles scheduling, auto-discovery, and repository cleanup so your backups keep running while you sleep.
Requirements
- Gitea Mirror deployment with outbound HTTPS access
- GitHub PAT + Gitea token stored in the UI or supplied via environment variables
- A monitoring target that can poll HTTP endpoints (Healthchecks.io, Uptime Kuma, Prometheus, etc.)
Step-by-step
1. Enable automatic syncing
- Go to Configuration → Automation.
- Toggle Automatic syncing on and choose an interval that matches your recovery point objective (start with
30 minutesfor active teams, stretch to12 hoursfor archives). - Confirm the scheduler is running by checking the Last sync and Next sync timestamps in the Automation card.
2. Keep the repository list current
- In Configuration → Connections, click Import GitHub Data so the dashboard knows about every repository, organization, and star you selected.
- Enable Mirror starred repositories if you want personal favorites backed up, and set the Starred repos organization for tidy storage in Gitea.
- Use the inline destination editor on the Repositories page when you need a repo to land in a different Gitea organization.
3. Configure repository cleanup (optional)
- Still on Configuration → Automation, enable Handle orphaned repositories automatically.
- Leave the action on Archive to keep a read-only backup when a GitHub repo disappears, or switch to Delete if you require a strict mirror.
- Disable Dry run after your first test so the cleanup service can act on what it finds.
4. Monitor scheduler health
- Point your monitoring system at
http://<mirror-host>:4321/api/healthto track uptime. - Review sync failures from the Activity Log page or export them via
/api/eventsfor long-term retention. - Run
bun run manage-db checkduring maintenance windows to verify background tasks, migrations, and queue state.
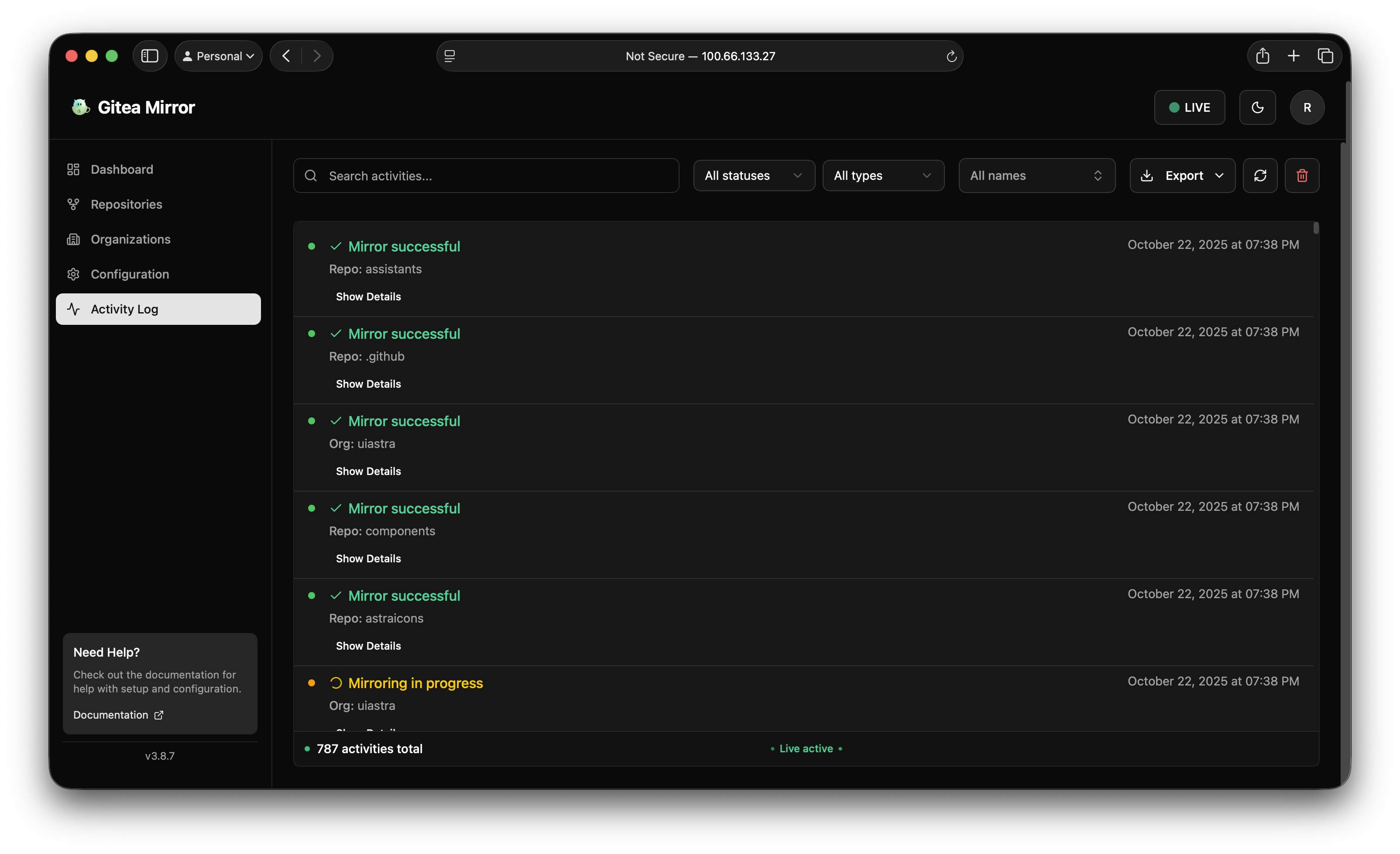
The Activity Log highlights successful syncs and failures so you can react before GitHub backups fall behind.
5. Harden credentials and runbooks
- Store GitHub and Gitea tokens via the Configuration UI—Gitea Mirror encrypts them at rest.
- Rotate tokens on a schedule and note expiry dates in your homelab runbook; the dashboard surfaces failures when credentials expire.
- Export the configuration JSON (
/api/export) alongside your documentation so you can rebuild the mirror quickly if you need to redeploy.
Validate automation
- Force a failure by temporarily revoking a PAT; the next scheduler run should flag the repository in the Activity Log. Restore the token and use Sync Repository to confirm recovery.
- Run
bun run manage-db check(or the UI health check) to ensure migrations and tasks are clean. - Spot-check the Repositories table or export the Activity Log CSV to confirm
Last mirroredtimestamps match your configured interval.
Best practices
- Tune the sync interval to balance freshness with GitHub rate limits; most homelabs sit between 30 and 120 minutes.
- Start with the cleanup action set to Archive until you are confident you will not remove something you still need.
- Pair automation with the Preserve GitHub History playbook to maintain context, not just code.
Related playbooks
FAQ
What replaces my cron scripts?
The built-in scheduler handles intervals, retries, and discovery. It also powers cleanup for deleted upstream repos (Archive/Delete) once enabled.
How do I get alerts if backups fail?
Monitor /api/health with Healthchecks.io or Uptime Kuma and review the Activity Log. You can export failures via /api/events for centralized logging.
Will new repositories be discovered automatically?
Yes. After importing your GitHub data once, the scheduler’s discovery step keeps the inventory updated and mirrors new repositories on the next run.
